Virtual Users And Domains With Postfix, Courier And MySQL (Debian Etch) - Page 6
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
On this page
13 Populate The Database And Test
To populate the database you can use the MySQL shell:
mysql -u root -p
USE mail;
At least you have to create entries in the tables domains and users:
INSERT INTO `domains` (`domain`) VALUES ('example.com');
INSERT INTO `users` (`email`, `password`, `quota`) VALUES ('sales@example.com', ENCRYPT('secret'), 10485760);(Please take care you use the ENCRYPT syntax in the second INSERT statement in order to encrypt the password!)
If you want to make entries in the other two tables, that would look like this:
INSERT INTO `forwardings` (`source`, `destination`) VALUES ('info@example.com', 'sales@example.com');
INSERT INTO `transport` (`domain`, `transport`) VALUES ('example.com', 'smtp:mail.example.com');
To leave the MySQL shell, type
quit;
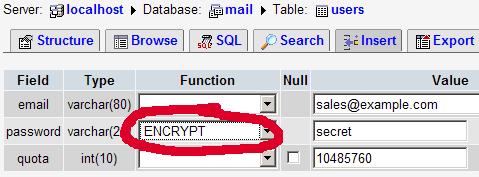
For most people it is easier if they have a graphical front-end to MySQL; therefore you can also use phpMyAdmin (in this example under http://192.168.0.100/phpmyadmin/ or http://server1.example.com/phpmyadmin/) to administrate the mail database. Again, when you create a user, go sure that you use the ENCRYPT function to encrypt the password:
I do not think I have to explain the domains and users table further.
The forwardings table can have entries like the following:
| source | destination | |
| info@example.com | sales@example.com | Redirects emails for info@example.com to sales@example.com |
| @example.com | thomas@example.com | Creates a Catch-All account for thomas@example.com. All emails to example.com will arrive at thomas@example.com, except those that exist in the users table (i.e., if sales@example.com exists in the users table, mails to sales@example.com will still arrive at sales@example.com). |
| @example.com | @anotherdomain.tld | This redirects all emails to example.com to the same user at anotherdomain.tld. E.g., emails to thomas@example.com will be forwarded to thomas@anotherdomain.tld. |
| info@example.com | sales@example.com, billing@anotherdomain.tld | Forward emails for info@example.com to two or more email addresses. All listed email addresses under destination receive a copy of the email. |
The transport table can have entries like these:
| domain | transport | |
| example.com | : | Delivers emails for example.com locally. This is as if this record would not exist in this table at all. |
| example.com | smtp:mail.anotherdomain.tld | Delivers all emails for example.com via smtp to the server mail.anotherdomain.com. |
| example.com | smtp:mail.anotherdomain.tld:2025 | Delivers all emails for example.com via smtp to the server mail.anotherdomain.com, but on port 2025, not 25 which is the default port for smtp. |
| example.com |
smtp:[1.2.3.4] |
The square brackets prevent Postfix from doing lookups of the MX DNS record for the address in square brackets. Makes sense for IP addresses. |
| .example.com | smtp:mail.anotherdomain.tld | Mail for any subdomain of example.com is delivered to mail.anotherdomain.tld. |
| * | smtp:mail.anotherdomain.tld | All emails are delivered to mail.anotherdomain.tld. |
| joe@example.com | smtp:mail.anotherdomain.tld | Emails for joe@example.com are delivered to mail.anotherdomain.tld. |
See
man transport
for more details.
Please keep in mind that the order of entries in the transport table is important! The entries will be followed from the top to the bottom.
Important: Postfix uses a caching mechanism for the transports, therefore it might take a while until you changes in the transport table take effect. If you want them to take effect immediately, run
postfix reload
after you have made your changes in the transport table.
14 References
- Tutorial: ISP-style Email Service with Debian-Sarge and Postfix 2.1: http://workaround.org/articles/ispmail-sarge/
- Postfix + Quota: http://vhcs.net/new/modules/newbb/viewtopic.php?topic_id=3496&forum=17
- Mail Passwords Encrypted using saslauthd: http://www.syscp.de/docs/public/contrib/cryptedmailpws
15 Links
- Postfix MTA: http://www.postfix.org/
- Postfix Quota Patch: http://web.onda.com.br/nadal/
- phpMyAdmin: http://www.phpmyadmin.net/
- Debian: http://www.debian.org/